Perennialism
In today’s world, the internet is saturated with information—so much so that almost anything can be made to appear true. So where do we turn for trustworthy answers?
This site exists to help people reclaim their sense of agency by offering tools for developing critical thinking. Science remains our most reliable method for understanding the external world. Yet when it comes to the rich terrain of inner experience—the realm of meaning, consciousness, and subjective truth—science often falls short.
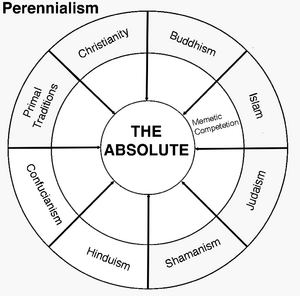
This is where Perennialism provides a grounding perspective. Perennialism suggests that if an idea is truly valid, it will endure the test of time, surviving centuries of scrutiny across cultures and civilizations. It values truths that persist not by force, but through the strength of their insight. By revisiting timeless aphorisms and enduring wisdom, we can uncover insights that continue to resonate today. In the psychedelic movement, this perspective reemerged during the 1960s and ’70s counterculture. At places like Esalen in California, a new vision emerged—what some called “the religion of no religion.” It embraced the idea that there are many paths up the same mountain, each pointing toward the same deeper truth.
Below are some short aphorisms, concise statement of insightful or moral reflection.
Aphorisms
An aphorism is a brief, memorable saying that expresses a general truth or principle.
- “If all you have is a hammer, everything looks like a nail.” This saying, like the many others listed below highlight a specific Cognitive Bias, in this case Attention Bias – which is the tendency to focus on what is most readily available or familiar while ignoring alternative possibilities.
- “The first impression is the last impression.” Bias: Anchoring Bias – Over-relying on the first piece of information encountered when making decisions.
- “Birds of a feather flock together.” Bias: Groupthink – The tendency to favor those who are similar or part of the same group as oneself.
- “What is popular is not always right, and what is right is not always popular.” Bias: Bandwagon Effect – Adopting beliefs or behaviors simply because many others do.
- “It worked last time, so it must work this time.” Bias: Availability Bias – Giving undue weight to recent events when making decisions.
- “Hindsight is always 20/20.” Bias: Hindsight Bias – The tendency to see past events as predictable after they have already happened.
- “Don’t judge a book by its cover.” Bias: Halo Effect – Allowing an overall impression (positive or negative) to influence judgments about unrelated aspects.