Saccade: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
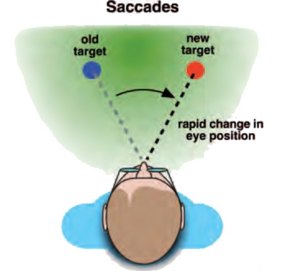
'''A saccade is a rapid eye movement that allows the high-resolution center of the retina (the fovea) to scan the environment.''' These unconscious shifts enable the brain to stitch together a high-definition mental simulation of the world around us. | '''A saccade is a rapid eye movement that allows the high-resolution center of the retina (the fovea) to scan the environment.''' These unconscious shifts enable the brain to stitch together a high-definition mental simulation of the world around us. | ||
The brain assembles saccade fragments into a seamless and stable mental representation of the world. This internal simulation feels continuous and complete, despite being constructed from partial, momentary glimpses. Over time, this stitched-together image becomes so convincing that we mistake it for objective reality itself, unaware that what we "see" is in fact a mental construct—filtered, interpreted, and heavily influenced by attention, memory, and expectation. | The brain assembles saccade fragments into a seamless and stable mental representation of the world. This internal simulation feels continuous and complete, despite being constructed from partial, momentary glimpses. Over time, this stitched-together image becomes so convincing that we mistake it for objective reality itself, unaware that what we "see" is in fact a mental construct—filtered, interpreted, and heavily influenced by attention, memory, and expectation. This is called the [[The Objectivity Assumption|Objectivity Assumption]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 23:13, 10 April 2025
A saccade is a rapid eye movement that allows the high-resolution center of the retina (the fovea) to scan the environment. These unconscious shifts enable the brain to stitch together a high-definition mental simulation of the world around us.
The brain assembles saccade fragments into a seamless and stable mental representation of the world. This internal simulation feels continuous and complete, despite being constructed from partial, momentary glimpses. Over time, this stitched-together image becomes so convincing that we mistake it for objective reality itself, unaware that what we "see" is in fact a mental construct—filtered, interpreted, and heavily influenced by attention, memory, and expectation. This is called the Objectivity Assumption.