Psychedelic Anxiety Syndrome: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=== Exposure Therapy === | === Exposure Therapy === | ||
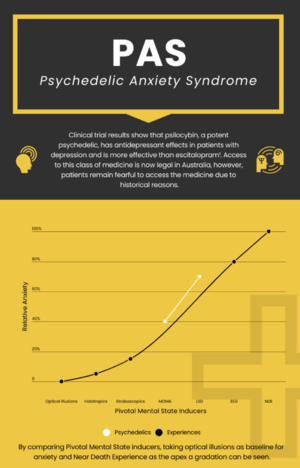
It is thought by introducing patients to controlled versions of different parts of the psychedelic experience anxiety can be substantially decreased. | It is thought by introducing patients to controlled versions of different parts of the psychedelic experience anxiety can be substantially decreased. This is done by subdividing the psychedelic experience into subsections and then rating them against perceived anxiety (See '''Figure 1'''), these include: | ||
* Optical illusions | |||
* Holotropics | |||
* Stroboscopics | |||
* Out of body experiences | |||
* Astral projections | |||
The ultimate goal is to allow the public to participate in a series of controlled experiments within the physical showing of the Fundamentals of Psychedelics lecture series. | |||
Revision as of 12:22, 18 October 2022
Psychedelic Anxiety Syndrome or PAS is the anxiety one feels before taking a psychedelic. Whilst in some cases PAS is warranted as there have been reports of negative effects to psychedelics, it is argued in many cases the anxiety felt is disproportionate to the benefits one might encounter.
Exposure Therapy
It is thought by introducing patients to controlled versions of different parts of the psychedelic experience anxiety can be substantially decreased. This is done by subdividing the psychedelic experience into subsections and then rating them against perceived anxiety (See Figure 1), these include:
- Optical illusions
- Holotropics
- Stroboscopics
- Out of body experiences
- Astral projections
The ultimate goal is to allow the public to participate in a series of controlled experiments within the physical showing of the Fundamentals of Psychedelics lecture series.