Neuroplasticity: Difference between revisions
From BurnZero
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Neuroplasticity.png|alt=Neuroplasticity|thumb|Neuroplasticity Vs Age.]] | [[File:Neuroplasticity.png|alt=Neuroplasticity|thumb|Neuroplasticity Vs Age.]] | ||
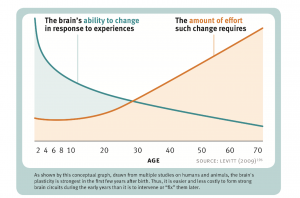
'''Neuroplasticity is the ability of the brain to change its default activity in response to intrinsic or extrinsic stimuli by reorganizing its structure, functions, or connections. Humans lose their neuroplasticity as they age.<ref>'''Changes in plasticity across the lifespan''': Cause of disease and target for intervention. Accessed on 3rd March 2022, via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4392917/</ref>''' Think of our brain circuitry like hiking trails. The ones that get a lot of traffic get smoother and wider, with brush stomped down and pushed back. The neural pathways that sit fallow grow over, becoming less likely to be used. | '''Neuroplasticity is the ability of the brain to change its default activity in response to intrinsic or extrinsic stimuli by reorganizing its structure, functions, or connections. Humans lose their neuroplasticity as they age.<ref>'''Changes in plasticity across the lifespan''': Cause of disease and target for intervention. Accessed on 3rd March 2022, via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4392917/</ref>''' | ||
Think of our brain circuitry like hiking trails. The ones that get a lot of traffic get smoother and wider, with brush stomped down and pushed back. The neural pathways that sit fallow grow over, becoming less likely to be used. | |||
There are ways to increase neuroplasticity temporarily via [[shock]] which can help people learn new ways. | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
Revision as of 04:00, 27 May 2022
Neuroplasticity is the ability of the brain to change its default activity in response to intrinsic or extrinsic stimuli by reorganizing its structure, functions, or connections. Humans lose their neuroplasticity as they age.[1]
Think of our brain circuitry like hiking trails. The ones that get a lot of traffic get smoother and wider, with brush stomped down and pushed back. The neural pathways that sit fallow grow over, becoming less likely to be used.
There are ways to increase neuroplasticity temporarily via shock which can help people learn new ways.
References
- ↑ Changes in plasticity across the lifespan: Cause of disease and target for intervention. Accessed on 3rd March 2022, via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4392917/