Confirmation Bias: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "'''Confirmation bias''' is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values<ref>https://pa...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
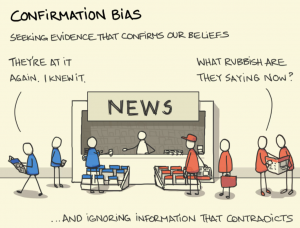
'''Confirmation bias''' is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values<ref>https://pages.ucsd.edu/~mckenzie/nickersonConfirmationBias.pdf</ref>. | [[File:Confirmation bias.png|alt=Confirmation bias|thumb|Reinforcing what we already think.]] | ||
'''Confirmation bias''' is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values<ref>https://pages.ucsd.edu/~mckenzie/nickersonConfirmationBias.pdf</ref>. Confirmation bias is the big one. The bias that leads us to live in a world of our own choosing, finding the information that already fits with our beliefs and ignoring or discounting what doesn't. It's the bias that makes two sides get further apart rather than closer together. | |||
Edward De Bono in Water Logic suggested a metaphor for thought as channels of water. As water runs through the channels the channels get deeper, and as they get deeper it pulls more of the water into the main channels until there is only one way. Confirmation bias can act like that. | |||
It's important to work to understand different opinions, not discount them upfront. To use our empathy to understand why others feel the way they do. And when we deliberately seek out information that challenges our point of view we will usually find a richer, more nuanced world that helps build bridges with others rather than drive us apart. | |||
'''References''' | |||
Revision as of 01:03, 20 April 2022
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values[1]. Confirmation bias is the big one. The bias that leads us to live in a world of our own choosing, finding the information that already fits with our beliefs and ignoring or discounting what doesn't. It's the bias that makes two sides get further apart rather than closer together.
Edward De Bono in Water Logic suggested a metaphor for thought as channels of water. As water runs through the channels the channels get deeper, and as they get deeper it pulls more of the water into the main channels until there is only one way. Confirmation bias can act like that.
It's important to work to understand different opinions, not discount them upfront. To use our empathy to understand why others feel the way they do. And when we deliberately seek out information that challenges our point of view we will usually find a richer, more nuanced world that helps build bridges with others rather than drive us apart.
References