Pivotal Mental States: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
m (→Psychedelics) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:Pivotal mental states induced by psychedelics.png|alt=Pivotal mental states induced by psychedelics|thumb|'''Figure 1'''. Pivotal mental states induced by psychedelics<ref>'''Ketamine psychedelic psychotherapy: Focus on its pharmacology, phenomenology, and clinical applications.''' Kolp, E., Friedman, H. L., Krupitsky, E., Jansen, K., Sylvester, M., Young, M. S., & Kolp, A. (2014). ''International Journal of Transpersonal Studies, 33''(2), 84–140. Accessed on 24th September 2022 via: https://digitalcommons.ciis.edu/ijts-transpersonalstudies/vol33/iss2/8/</ref>.]] | [[File:Pivotal mental states induced by psychedelics.png|alt=Pivotal mental states induced by psychedelics|thumb|'''Figure 1'''. Pivotal mental states induced by psychedelics<ref>'''Ketamine psychedelic psychotherapy: Focus on its pharmacology, phenomenology, and clinical applications.''' Kolp, E., Friedman, H. L., Krupitsky, E., Jansen, K., Sylvester, M., Young, M. S., & Kolp, A. (2014). ''International Journal of Transpersonal Studies, 33''(2), 84–140. Accessed on 24th September 2022 via: https://digitalcommons.ciis.edu/ijts-transpersonalstudies/vol33/iss2/8/</ref>.]] | ||
=== Psychedelics === | === Psychedelics === | ||
[[Psychedelics]] are medicines that when administered under [[Psychedelic Best Practice|Best Practice]] can safely and proundly shift normal thought patterns<ref>'''From Egoism to Ecoism: Psychedelics Increase Nature Relatedness in a State-Mediated and Context-Dependent Manner.''' Kettner H, Gandy S, Haijen ECHM, Carhart-Harris RL. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 16;16(24):5147. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16245147. PMID: 31888300; PMCID: PMC6949937. Accessed on 24th September 2022 via https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/16/24/5147</ref> (see '''Figure 1'''). This is achieved by | [[Psychedelics]] are medicines that when administered under [[Psychedelic Best Practice|Best Practice]] can safely and proundly shift normal thought patterns<ref>'''From Egoism to Ecoism: Psychedelics Increase Nature Relatedness in a State-Mediated and Context-Dependent Manner.''' Kettner H, Gandy S, Haijen ECHM, Carhart-Harris RL. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 16;16(24):5147. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16245147. PMID: 31888300; PMCID: PMC6949937. Accessed on 24th September 2022 via https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/16/24/5147</ref> (see '''Figure 1'''). This is achieved by temporarily altering brain function to be less constrained than usual by modulating the presence or absence of underlying anatomical connections<ref>'''LSD alters dynamic integration and segregation in the human brain''', NeuroImage, Volume 227, 2021, 117653, ISSN 1053-8119, Andrea I. Luppi, Robin L. Carhart-Harris, Leor Roseman, Ioannis Pappas, David K. Menon, Emmanuel A. Stamatakis,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117653.Accessed on 24th Sept 2022 via https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811920311381 </ref>. There is now a vast amount of evidence to suggest that psychedelics are highly effective in treating mental health conditions such as addiction, depression and anxiety<ref>'''Adverse effects of psychedelics: From anecdotes and misinformation to systematic science.''' Anne K Schlag, Jacob Aday, Iram Salam. First Published February 2, 2022. [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/02698811211069100 https://doi.org/10.1177/02698811211069100]</ref>. | ||
===Electroconvulsive Therapy=== | ===Electroconvulsive Therapy=== | ||
[[Electroconvulsive Therapy|Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)]] is a technique used in modern medicine to cure treatment resistant depression patients. Research has shown that 64% to 87% of patients with severe depression respond to ECT, with response rates as high as 95% for patients that have accompanying psychotic features<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4193538/</ref>. There is some evidence to suggest that ECT causes similar long and short term effects to [[psychedelics]] in some in vivo case studies<ref>Psychotic symptoms as a complication of electroconvulsive therapy – a case report Anna Antosik-Wójcińska, Magdalena Chojnacka, Łukasz Święcicki Affective Disorders Unit, Second Department of Psychiatry, Institute of Psychiatry and Neurology in Warsaw</ref><ref>'''ECT associated musical hallucinations in an elderly patient''': a case report. ''Ann Gen Psychiatry'' 5, 10 (2006). Janakiraman, R., Wildgoose, K. & Seelam, K. <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-859X-5-10</nowiki></ref><ref>'''LSD-Like Flashbacks Associated with ECT'''. Convuls Ther. Russ MJ, Gold JM. . 1987;3(4):296-301. PMID: 11940932. Accessed on 4th July 2022 via: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11940932/</ref>. | [[Electroconvulsive Therapy|Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)]] is a technique used in modern medicine to cure treatment resistant depression patients. Research has shown that 64% to 87% of patients with severe depression respond to ECT, with response rates as high as 95% for patients that have accompanying psychotic features<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4193538/</ref>. There is some evidence to suggest that ECT causes similar long and short term effects to [[psychedelics]] in some in vivo case studies<ref>Psychotic symptoms as a complication of electroconvulsive therapy – a case report Anna Antosik-Wójcińska, Magdalena Chojnacka, Łukasz Święcicki Affective Disorders Unit, Second Department of Psychiatry, Institute of Psychiatry and Neurology in Warsaw</ref><ref>'''ECT associated musical hallucinations in an elderly patient''': a case report. ''Ann Gen Psychiatry'' 5, 10 (2006). Janakiraman, R., Wildgoose, K. & Seelam, K. <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-859X-5-10</nowiki></ref><ref>'''LSD-Like Flashbacks Associated with ECT'''. Convuls Ther. Russ MJ, Gold JM. . 1987;3(4):296-301. PMID: 11940932. Accessed on 4th July 2022 via: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11940932/</ref>, however ECT can cause memory loss in some patients. | ||
=== Overview Effect === | === Overview Effect === | ||
Astronauts looking back at Earth with the naked eye often suddenly get an overwhelming responsibility to protect it. When they see only a fine blue line of atmosphere that shelters our only planet from the hostile vacuum of space, national borders disappear; and the scene often evokes a feeling of cosmic connection. This so-called “''overview effect''” has been turning astronauts into environmental advocates ever since the first person in space. | Astronauts looking back at Earth with the naked eye often suddenly get an overwhelming responsibility to protect it. When they see only a fine blue line of atmosphere that shelters our only planet from the hostile vacuum of space, national borders disappear; and the scene often evokes a feeling of cosmic connection. This so-called “''overview effect''” has been turning astronauts into environmental advocates ever since the first person in space. | ||
Revision as of 00:47, 29 November 2022
Pivotal Mental States (PiMS) are states of mind created by profound psychological events which shift default thought patterns. PiMS are an evolved feature of human brains as they aid in overwriting outdated ways of thinking when novel, actual or perceived environmental pressures demand this[1]. PiMS exert their effect by inducing neuroplastic states, which given the correct priming, setting and integration allows the user to eliminate out-of-date thought patterns and strengthen healthier, more adapted ones. Specific PiMS have been shown clinically to ease psychological transitions away from egocentrism toward ecocentrism[2][3][4].
Below is a list of known PiM inducers listed in order of ease of accessibility:
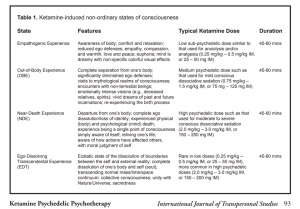
Psychedelics
Psychedelics are medicines that when administered under Best Practice can safely and proundly shift normal thought patterns[6] (see Figure 1). This is achieved by temporarily altering brain function to be less constrained than usual by modulating the presence or absence of underlying anatomical connections[7]. There is now a vast amount of evidence to suggest that psychedelics are highly effective in treating mental health conditions such as addiction, depression and anxiety[8].
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a technique used in modern medicine to cure treatment resistant depression patients. Research has shown that 64% to 87% of patients with severe depression respond to ECT, with response rates as high as 95% for patients that have accompanying psychotic features[9]. There is some evidence to suggest that ECT causes similar long and short term effects to psychedelics in some in vivo case studies[10][11][12], however ECT can cause memory loss in some patients.
Overview Effect
Astronauts looking back at Earth with the naked eye often suddenly get an overwhelming responsibility to protect it. When they see only a fine blue line of atmosphere that shelters our only planet from the hostile vacuum of space, national borders disappear; and the scene often evokes a feeling of cosmic connection. This so-called “overview effect” has been turning astronauts into environmental advocates ever since the first person in space.
Yuri Gagarin, upon his return as the first human in space, marvelled at the planet from orbit in 1961. “People of the world, let us safeguard and enhance this beauty — not destroy it,” . A half-century later, ex-NASA astronaut José Hernández said that the view aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery in 2009 turned him into “an instant treehugger.” On Christmas Eve 1968, NASA astronauts Frank Borman, Jim Lovell and William Anders were aboard Apollo 8, the first manned mission to orbit the Moon. They had spent most of the day photographing the Moon’s surface when Borman turned the spaceship around, and Earth came into view. ‘Oh my God, look at that picture over there. Here’s the Earth coming up,’ shouted Anders. Like the astronauts themselves, the world was awestruck by the first images of the whole Earth from space, which are today widely credited with triggering the birth of the modern environmental movement.
Near Death Experience
A Near-death-experience (NDE) is an intense psychological experience characterized by an atypical state of consciousness typically experience during life-threatening conditions[13]. NDEs in general are typically characterised by Out of Body Experiences and hallucinations[14][15] which are affected by set and setting much like psychedelics[16]. The after effects of an NDEs have been widely documented and have been shown to be powerfully life-altering.
Pivotal Mentals States Precursors
Optical Illusions
Whilst one of the weakest ways to induce PiMS, optical illusions can provide a gateway for people to start to ask elementary questions about their perceptions and start them on the path to overcome their Psychedelic Anxiety Syndrome.
Stroboscopics
Stroboscopics is a technique that flashes a bright light into the eyes of patients that in turn induces visual hallucinations. The process works as the speed at which the light is flashing is the same speed as the transmission rate of the optical nerve, this causes an temporary interference pattern which disorientates optical transmission to the brain leading to visual hallucinations similar to effects induced by psychedelic substances[17].
Spiritual experiences
Whilst unproven scientifically, (it would be very difficult due to the subjective nature) spiritual experiences have been shown to shift modes of general thought patterns. Pharmacologically the human brain has been found to produce endogenous psychedelic compounds (DMT)[18], some believe that certain techniques may be helpful in unleashing its effect:
- Holotropic breathing techniques[19][20] - 30 minutes breathing in a controlled, three-beat pattern — one sharp breath into my belly, one sharp breath into my lungs, and a sigh-like exhale to release.
References
- ↑ Pivotal mental states. Brouwer A, Carhart-Harris RL. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2021;35(4):319-352. doi:10.1177/0269881120959637. Accessed on 24th September 2022 via https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0269881120959637
- ↑ From Egoism to Ecoism: Psychedelics Increase Nature Relatedness in a State-Mediated and Context-Dependent Manner. Hannes Kettner, Sam Gandy, Eline C. H. M. Haijen and Robin L. Carhart-Harris Centre for Psychedelic Research, Department of Brain Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. Published: December 2019 DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16245147. Accessed on 30th September 2022 via: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31888300/
- ↑ Lifetime experience with (classic) psychedelics predicts pro-environmental behavior through an increase in nature relatedness. Matthias Forstmann and Christina Sagioglou Journal of Psychopharmacology 2017. DOI: 10.1177/0269881117714049. Accessed on 30th September 2022 via: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28631526/
- ↑ Manifesting Minds: A Review of Psychedelics in Science, Medicine, Sex, and Spirituality. Doblin, Rick; Brad Burge (2014) North Atlantic Books. ISBN 1583947272.
- ↑ Ketamine psychedelic psychotherapy: Focus on its pharmacology, phenomenology, and clinical applications. Kolp, E., Friedman, H. L., Krupitsky, E., Jansen, K., Sylvester, M., Young, M. S., & Kolp, A. (2014). International Journal of Transpersonal Studies, 33(2), 84–140. Accessed on 24th September 2022 via: https://digitalcommons.ciis.edu/ijts-transpersonalstudies/vol33/iss2/8/
- ↑ From Egoism to Ecoism: Psychedelics Increase Nature Relatedness in a State-Mediated and Context-Dependent Manner. Kettner H, Gandy S, Haijen ECHM, Carhart-Harris RL. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 16;16(24):5147. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16245147. PMID: 31888300; PMCID: PMC6949937. Accessed on 24th September 2022 via https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/16/24/5147
- ↑ LSD alters dynamic integration and segregation in the human brain, NeuroImage, Volume 227, 2021, 117653, ISSN 1053-8119, Andrea I. Luppi, Robin L. Carhart-Harris, Leor Roseman, Ioannis Pappas, David K. Menon, Emmanuel A. Stamatakis,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117653.Accessed on 24th Sept 2022 via https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811920311381
- ↑ Adverse effects of psychedelics: From anecdotes and misinformation to systematic science. Anne K Schlag, Jacob Aday, Iram Salam. First Published February 2, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/02698811211069100
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4193538/
- ↑ Psychotic symptoms as a complication of electroconvulsive therapy – a case report Anna Antosik-Wójcińska, Magdalena Chojnacka, Łukasz Święcicki Affective Disorders Unit, Second Department of Psychiatry, Institute of Psychiatry and Neurology in Warsaw
- ↑ ECT associated musical hallucinations in an elderly patient: a case report. Ann Gen Psychiatry 5, 10 (2006). Janakiraman, R., Wildgoose, K. & Seelam, K. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-859X-5-10
- ↑ LSD-Like Flashbacks Associated with ECT. Convuls Ther. Russ MJ, Gold JM. . 1987;3(4):296-301. PMID: 11940932. Accessed on 4th July 2022 via: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11940932/
- ↑ The phenomenology of near-death experiences. Am. J. Psychiatry 137, 1193–1196. Greyson, B., and Stevenson, I. (1980). Accessed on 24th September 2022 via https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7416264/
- ↑ Near-Death Experiences are Hallucinations. Keith Augustine. In Keith Augustine & Michael Martin (eds.), The Myth of an Afterlife: The Case against Life After Death. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 529-569 (2015)
- ↑ Three cases of near death experience: Is it physiology, physics or philosophy? Purkayastha M, Mukherjee KK. Ann Neurosci. 2012 Jul;19(3):104-6. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.190303. PMID: 25205979; PMCID: PMC4117086.
- ↑ Comparison of psychedelic and near-death or other non-ordinary experiences in changing attitudes about death and dying. Mary M. Sweeney ,Sandeep Nayak,Ethan S. Hurwitz, Lisa N. Mitchell,T. Cody Swift,Roland R. Griffiths. Published: August 24, 2022. Accessed on 26th August 2022 via https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0271926
- ↑ Altered states phenomena induced by visual flicker light stimulation. Marie Therese Bartossek, Johanna Kemmerer, Timo Torsten Schmidt. Published: July 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0253779
- ↑ N, N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), an Endogenous Hallucinogen: Past, Present, and Future Research to Determine Its Role and Function. Front Neurosci. 2018; 12: 536. Published online 2018 Aug 6. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00536. Accessed on 24th September via: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6088236
- ↑ https://maps.org/news-letters/v23n1/v23n1_24-27.pdf
- ↑ https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00353/full