Neuroplasticity: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Neuroplasticity.png|alt=Neuroplasticity|thumb|'''Figure 1'''. Neuroplasticity Vs Age.]] | [[File:Neuroplasticity.png|alt=Neuroplasticity|thumb|'''Figure 1'''. Neuroplasticity Vs Age.]] | ||
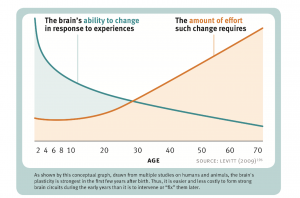
'''Neuroplasticity is the ability of the brain to change its default activity in response to stimuli by reorganizing how it works by modifying its connectivity. Humans lose their neuroplasticity peaking at 35 years of age<ref>'''Changes in plasticity across the lifespan''': Cause of disease and target for intervention. Accessed on 3rd March 2022, via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4392917/</ref> (see''' '''figure 1), recent studies have shown this can be temporarily reversed by types of [[shock]].''' | |||
'''Neuroplasticity is the ability of the brain to change its default activity in response to stimuli by reorganizing how it works by modifying its connectivity. Humans lose their neuroplasticity peaking at 35 years of age<ref>'''Changes in plasticity across the lifespan''': Cause of disease and target for intervention. Accessed on 3rd March 2022, via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4392917/</ref> (see''' '''figure 1) | |||
The brain is [[Neurochemistry|neurochemical]] in nature, meaning it is part ''chemical'' and part ''electric''. When | The brain is [[Neurochemistry|neurochemical]] in nature, meaning it is part ''chemical'' and part ''electric''. When these systems combine they work like hiking trails; the pathways that get a lot of traffic get smoother and wider, with brush stomped down and pushed back. The neural pathways that sit unused grow over, becoming less likely to be used. Your brain uses the more accessible pathways as it takes [[Energy frugal brain|lower energy]] to do so. In times of [[Ecological crisis|crisis]] people nimble on their feet are of paramount importance. | ||
=== References === | === References === | ||
Revision as of 08:56, 16 June 2022
Neuroplasticity is the ability of the brain to change its default activity in response to stimuli by reorganizing how it works by modifying its connectivity. Humans lose their neuroplasticity peaking at 35 years of age[1] (see figure 1), recent studies have shown this can be temporarily reversed by types of shock.
The brain is neurochemical in nature, meaning it is part chemical and part electric. When these systems combine they work like hiking trails; the pathways that get a lot of traffic get smoother and wider, with brush stomped down and pushed back. The neural pathways that sit unused grow over, becoming less likely to be used. Your brain uses the more accessible pathways as it takes lower energy to do so. In times of crisis people nimble on their feet are of paramount importance.
References
- ↑ Changes in plasticity across the lifespan: Cause of disease and target for intervention. Accessed on 3rd March 2022, via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4392917/