Setting: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Setting | '''Setting, a concept developed by Timothy Leary<ref>'''Constructing drug effects: A history of set and setting'''. Drug Science, Policy and Law. Ido Hartogsohn First Published January 1, 2017 <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1177/2050324516683325</nowiki></ref>, refers to the physical environment in which [[psychedelics]] are consumed.''' This is distinct from [[priming]], which relates to the mental state before drug administration. While initially applied in psychedelic research, these concepts have also proven useful in studying the effects of substances like alcohol, heroin, Ritalin, methamphetamine<ref>Dwyer, R, Moore, D (2013) Enacting multiple methamphetamines: the ontological politics of public discourse and consumer accounts of a drug and its effects. The International Journal on Drug Policy 24(3): 203–211.</ref>, cocaine, and crack cocaine<ref>Zinberg, NE (1984) Drug, Set, and Setting: The Basis for Controlled Intoxicant Use, 1st ed. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.</ref>. The key idea behind setting is that the location where a drug is taken can influence its effects, possibly through [[Psychosomatics|psychosomatic]] mechanisms. | ||
== Best Practice setting == | == Best Practice setting == | ||
Extensive medical research has been conducted to establish what are the best conditions for a [[Psychedelic Experience|psychedelic experience]]. Highlighted areas to address include<ref>'''Effects of Setting on Psychedelic Experiences, Therapies, and Outcomes''': A Rapid Scoping Review of the Literature. Chapter in Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences · February 2022 DOI: 10.1007/7854_2021_298 </ref>: | Extensive medical research has been conducted to establish what are the best conditions for a [[Psychedelic Experience|psychedelic experience]]. Highlighted areas to address include<ref>'''Effects of Setting on Psychedelic Experiences, Therapies, and Outcomes''': A Rapid Scoping Review of the Literature. Chapter in Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences · February 2022 DOI: 10.1007/7854_2021_298 </ref>: | ||
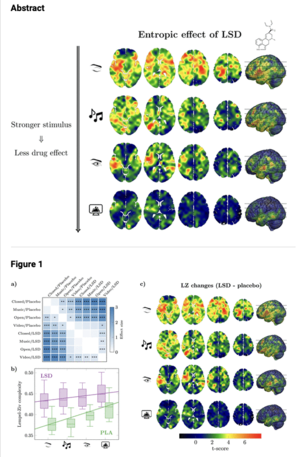
* '''Music''' - induces relaxation and stress reduction<ref>'''Set and Setting: A Randomized Study of Different Musical Genres in Supporting Psychedelic Therapy'''. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 2, 472–478, Publication Date:December 29, 2020, <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1021/acsptsci.0c00187</nowiki></ref><ref>'''Music and soulmaking toward a new theory of music therapy.''' Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. Crowe, B. (2004). de Araujo, D., Ribeiro, S., Cecchi, G. A., Carvalho, F. M., Sanchez, T. A., Pinto, J. P., et al. (2012). Seeing with the eyes shut: neural basis of enhanced imagery following ayahuasca ingestion. Hum. Brain Mapp. 33 (11), 2550–2560. doi:10.1002/hbm.21381</ref> whilst giving a time dependent medium for emotional expression<ref>'''“The neuroscience of emotion and music,” in Communicative musicality: exploring the basis of human companionship.''' Panksepp, J., and Trevarthen, C. (2009). Editors S. Malloch, and C. Trevarthen (Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 105–146.</ref>. | * [[File:Effects of music on psychedelic.png|alt=external stimulation and brain|thumb|'''Figure 1'''. By increasing external stimulation there is a narrower effect on the brain.]]'''[[Music and Psychedelic Experiences|Music]]''' - induces relaxation and stress reduction<ref>'''Set and Setting: A Randomized Study of Different Musical Genres in Supporting Psychedelic Therapy'''. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 2, 472–478, Publication Date:December 29, 2020, <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1021/acsptsci.0c00187</nowiki></ref><ref>'''Music and soulmaking toward a new theory of music therapy.''' Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. Crowe, B. (2004). de Araujo, D., Ribeiro, S., Cecchi, G. A., Carvalho, F. M., Sanchez, T. A., Pinto, J. P., et al. (2012). Seeing with the eyes shut: neural basis of enhanced imagery following ayahuasca ingestion. Hum. Brain Mapp. 33 (11), 2550–2560. doi:10.1002/hbm.21381</ref> whilst giving a time dependent medium for emotional expression<ref>'''“The neuroscience of emotion and music,” in Communicative musicality: exploring the basis of human companionship.''' Panksepp, J., and Trevarthen, C. (2009). Editors S. Malloch, and C. Trevarthen (Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 105–146.</ref>. However, one study has shown that listening to music decreases entropy and can potentially reduce the overall therapeutic effect (see '''Figure 1''')<ref>'''Effects of External Stimulation on Psychedelic State Neurodynamics.''' Mediano, Pedro A., Fernando E. Rosas, Christopher Timmermann, Leor Roseman, David J. Nutt, Amanda Feilding, Mendel Kaelen, et al. 2024. ''ACS Chemical Neuroscience'', January. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00289. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00289</ref>. | ||
* '''Lighting''' - most prefer psychedelic sessions at night and some it strange to start a ceremony at midday<ref>The Evolved Psychology of Psychedelic Set and Setting: Inferences Regarding the Roles of Shamanism and Entheogenic Ecopsychology. Front. Pharmacol., Published 23 February 2021, Sec. Ethnopharmacology. <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.619890</nowiki></ref>. It has been found that using a blindfold to reduce ambient light increases the intensity of the psychedelic experience<ref>https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00289#</ref>. | |||
* '''Lighting''' - most prefer psychedelic sessions at night and | *'''Physical attributes of the medicine''' - much like placebo, size, colour, smell; all contribute to the effect<ref>'''Set and setting, psychedelics and the placebo response''': An extra-pharmacological perspective on psychopharmacology. Ido Hartogsohn, Journal of Psychopharmacology | ||
*'''Physical attributes of the medicine''' - much like placebo size, colour, smell all contribute to the effect<ref>'''Set and setting, psychedelics and the placebo response''': An extra-pharmacological perspective on psychopharmacology. Ido Hartogsohn, Journal of Psychopharmacology | |||
2016. DOI: 10.1177/0269881116677852.</ref>. | 2016. DOI: 10.1177/0269881116677852.</ref>. | ||
*'''Fasting''' - to ensure pharmacokinetic stability, patients should fast for an average of 2-4 h (except water)<ref>'''Therapeutic use of psilocybin: Practical considerations for dosing and administration.''' MacCallum CA, Lo LA, Pistawka CA, Deol JK. Front Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 1;13:1040217. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1040217. PMID: 36532184; PMCID: PMC9751063. Accessed via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9751063/</ref>. | |||
*'''Singing''' - singing, whistling or drumming elicits oxytocin production a neurohormone enhancing calming and social bonding<ref>'''What’s missing from the scientific study of religion?''' Dunbar, R. (2017). ''Religion, Brain Behav.'' 7 (4), 349–353. doi:10.1080/2153599X.2016.1249927</ref>. | |||
==== Pre ==== | ==== Pre ==== | ||
Have an objective, don't just go in to get fucked because you will. A great goal is to | To reiterate, to get on the correct trajectory and enhance the therapeutic effect of psychedelic medicine, [[priming]] is of the utmost importance: "Have an objective, don't just go in to get fucked because you will. A great goal is to ''let go of anger and sadness and to be reminded of beauty and happiness''" - Sting | ||
==== During ==== | ==== During ==== | ||
Occasionally, time distorts however remember that it will be over. No matter what, you aren't going to die, you aren't going to go mad and the effects are not permanent. | [[File:Letting go during psychedelics.png|alt=Letting go during psychedelics|thumb|'''Figure 2'''. How to let go during a psychedelic experience.]] | ||
Remember to let go, the [[Psychedelic Experience|psychedelic experience]] will temporarily dissolve the neural pathways which make up how you perceive the world around you. However, it is easy to forget this and feel as if YOU are physically dissolving into the world around you (see '''Figure 2'''). Occasionally, time distorts however, remember that it will be over. No matter what, you aren't going to die, you aren't going to go mad and the effects are not permanent. | |||
==== Integration ==== | |||
[[Integration]] is the time immediately after the psychedelic experience, it is seen as a closing window of opportunity to integrate new thought patterns into the software of the brain. By employing various technique during the integration period specific positive effects of [[Psychedelics|psychedelic]] use can be maintained. | |||
=== Setting Modulation === | |||
Once the basics as above have been covered, it is possible to | Once the basics as above have been covered, it is possible to modulate you environment to see how the mind is effected. An simple place to start is to use a Psychedelic Visualisation Modulator, which can be used to explore the psychedelic effect on the visual field. | ||
====== Psychedelic Visualisation Modulators ====== | ====== Psychedelic Visualisation Modulators ====== | ||
| Line 107: | Line 112: | ||
|No | |No | ||
|} | |} | ||
====== Psychedelic Psychical Modulators ====== | |||
To enhance healing during a [[psilocybin]] or [[MDMA]] experiences, focus on releasing trauma stored in the body rather than overthinking problems. | |||
# About 30-60 minutes into the trip, when things may feel chaotic, stay calm and begin a self-massage technique. | |||
# Once you feel the psilocybin's effects, remove your shirt and start massaging your upper body. | |||
# Use your hands to apply different strokes or pressures across your shoulders, arms, chest, neck, and belly. Follow what feels good or right—whether gentle caressing or firmer pressure. | |||
# As you massage, old memories, emotions, or traumas may arise. This indicates that you're releasing negative energy from your body. Trauma is stored in your muscles, not your mind, so physical release through massage is key. | |||
# Continue until you feel you've released tension from all parts of your body. You might end up fully naked, addressing the areas that feel burdened by trapped emotions. | |||
==== After ==== | ==== After ==== | ||
This is the most important part of the psychedelic experience, afterwards you remain in a [[Neuroplasticity|neuroplastic]] state and have the ability to [[Integration|integrate]] what was learnt during the [[Psychedelic Experience|psychedelic experience]].'''References'''<references /> | This is the most important part of the psychedelic experience, afterwards you remain in a [[Neuroplasticity|neuroplastic]] state and have the ability to [[Integration|integrate]] what was learnt during the [[Psychedelic Experience|psychedelic experience]]. | ||
'''References'''<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:13, 4 October 2024
Setting, a concept developed by Timothy Leary[1], refers to the physical environment in which psychedelics are consumed. This is distinct from priming, which relates to the mental state before drug administration. While initially applied in psychedelic research, these concepts have also proven useful in studying the effects of substances like alcohol, heroin, Ritalin, methamphetamine[2], cocaine, and crack cocaine[3]. The key idea behind setting is that the location where a drug is taken can influence its effects, possibly through psychosomatic mechanisms.
Best Practice setting
Extensive medical research has been conducted to establish what are the best conditions for a psychedelic experience. Highlighted areas to address include[4]:
- Music - induces relaxation and stress reduction[5][6] whilst giving a time dependent medium for emotional expression[7]. However, one study has shown that listening to music decreases entropy and can potentially reduce the overall therapeutic effect (see Figure 1)[8].
- Lighting - most prefer psychedelic sessions at night and some it strange to start a ceremony at midday[9]. It has been found that using a blindfold to reduce ambient light increases the intensity of the psychedelic experience[10].
- Physical attributes of the medicine - much like placebo, size, colour, smell; all contribute to the effect[11].
- Fasting - to ensure pharmacokinetic stability, patients should fast for an average of 2-4 h (except water)[12].
- Singing - singing, whistling or drumming elicits oxytocin production a neurohormone enhancing calming and social bonding[13].
Pre
To reiterate, to get on the correct trajectory and enhance the therapeutic effect of psychedelic medicine, priming is of the utmost importance: "Have an objective, don't just go in to get fucked because you will. A great goal is to let go of anger and sadness and to be reminded of beauty and happiness" - Sting
During
Remember to let go, the psychedelic experience will temporarily dissolve the neural pathways which make up how you perceive the world around you. However, it is easy to forget this and feel as if YOU are physically dissolving into the world around you (see Figure 2). Occasionally, time distorts however, remember that it will be over. No matter what, you aren't going to die, you aren't going to go mad and the effects are not permanent.
Integration
Integration is the time immediately after the psychedelic experience, it is seen as a closing window of opportunity to integrate new thought patterns into the software of the brain. By employing various technique during the integration period specific positive effects of psychedelic use can be maintained.
Setting Modulation
Once the basics as above have been covered, it is possible to modulate you environment to see how the mind is effected. An simple place to start is to use a Psychedelic Visualisation Modulator, which can be used to explore the psychedelic effect on the visual field.
Psychedelic Visualisation Modulators
| Link | Summary | Settings | Interactive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hop Along | A never ending orbits visualizer. Use keys and mouse to increase speed and angle | Yes | Yes |
| Strobe | Stare at the middle for 30 seconds for to experience an optical illusion | No | No |
| Weavesilk | Generate art | Yes | Yes |
| Balls demo | Colorful balls that follow your mouse (Enable fullscreen for best effect) | Yes | Yes |
| Chromoscope | Explore the Milky Way in various wavelengths | Yes | Yes |
| Particle Dream | Particle visualization with many options | Yes | Yes |
| Cosmic Symbolism | Never ending cosmic zooming experience (click and drag for speed) | No | Yes |
| Draw A 3D Mandala | Draw a mandala with different colors in 3d | Yes | Yes |
| Mr Doob Harmony | Make art by sketching with different materials and colors (many more triptoys at the top of the page) | Yes | Yes |
| Fluids | Colorful physics demonstration of fluid | Yes | Yes |
| Water physics | Physics demonstration. Move around, drag the ball, ripple the water. | Yes | Yes |
| Arkadia | Never ending psychedelic forest | No | No |
| Puddle | Interact with paint-like soundwaves | No | Yes |
| A Way To Go | Draw lines and walk through a forest while creating music | No | Yes |
| Soft Murmur | Create your own mix of background noise | Yes | Yes |
| MyNoise.net | Ambient noise generator with a variety of themes from rain to black holes to busy cafe to kitten purrs. | Yes | No |
Psychedelic Psychical Modulators
To enhance healing during a psilocybin or MDMA experiences, focus on releasing trauma stored in the body rather than overthinking problems.
- About 30-60 minutes into the trip, when things may feel chaotic, stay calm and begin a self-massage technique.
- Once you feel the psilocybin's effects, remove your shirt and start massaging your upper body.
- Use your hands to apply different strokes or pressures across your shoulders, arms, chest, neck, and belly. Follow what feels good or right—whether gentle caressing or firmer pressure.
- As you massage, old memories, emotions, or traumas may arise. This indicates that you're releasing negative energy from your body. Trauma is stored in your muscles, not your mind, so physical release through massage is key.
- Continue until you feel you've released tension from all parts of your body. You might end up fully naked, addressing the areas that feel burdened by trapped emotions.
After
This is the most important part of the psychedelic experience, afterwards you remain in a neuroplastic state and have the ability to integrate what was learnt during the psychedelic experience.
References
- ↑ Constructing drug effects: A history of set and setting. Drug Science, Policy and Law. Ido Hartogsohn First Published January 1, 2017 https://doi.org/10.1177/2050324516683325
- ↑ Dwyer, R, Moore, D (2013) Enacting multiple methamphetamines: the ontological politics of public discourse and consumer accounts of a drug and its effects. The International Journal on Drug Policy 24(3): 203–211.
- ↑ Zinberg, NE (1984) Drug, Set, and Setting: The Basis for Controlled Intoxicant Use, 1st ed. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- ↑ Effects of Setting on Psychedelic Experiences, Therapies, and Outcomes: A Rapid Scoping Review of the Literature. Chapter in Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences · February 2022 DOI: 10.1007/7854_2021_298
- ↑ Set and Setting: A Randomized Study of Different Musical Genres in Supporting Psychedelic Therapy. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 2, 472–478, Publication Date:December 29, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsptsci.0c00187
- ↑ Music and soulmaking toward a new theory of music therapy. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. Crowe, B. (2004). de Araujo, D., Ribeiro, S., Cecchi, G. A., Carvalho, F. M., Sanchez, T. A., Pinto, J. P., et al. (2012). Seeing with the eyes shut: neural basis of enhanced imagery following ayahuasca ingestion. Hum. Brain Mapp. 33 (11), 2550–2560. doi:10.1002/hbm.21381
- ↑ “The neuroscience of emotion and music,” in Communicative musicality: exploring the basis of human companionship. Panksepp, J., and Trevarthen, C. (2009). Editors S. Malloch, and C. Trevarthen (Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 105–146.
- ↑ Effects of External Stimulation on Psychedelic State Neurodynamics. Mediano, Pedro A., Fernando E. Rosas, Christopher Timmermann, Leor Roseman, David J. Nutt, Amanda Feilding, Mendel Kaelen, et al. 2024. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, January. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00289. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00289
- ↑ The Evolved Psychology of Psychedelic Set and Setting: Inferences Regarding the Roles of Shamanism and Entheogenic Ecopsychology. Front. Pharmacol., Published 23 February 2021, Sec. Ethnopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.619890
- ↑ https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00289#
- ↑ Set and setting, psychedelics and the placebo response: An extra-pharmacological perspective on psychopharmacology. Ido Hartogsohn, Journal of Psychopharmacology 2016. DOI: 10.1177/0269881116677852.
- ↑ Therapeutic use of psilocybin: Practical considerations for dosing and administration. MacCallum CA, Lo LA, Pistawka CA, Deol JK. Front Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 1;13:1040217. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1040217. PMID: 36532184; PMCID: PMC9751063. Accessed via https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9751063/
- ↑ What’s missing from the scientific study of religion? Dunbar, R. (2017). Religion, Brain Behav. 7 (4), 349–353. doi:10.1080/2153599X.2016.1249927